Melones-Herrero J, Alcalá S, Ruiz-Cañas L, Benítez-Buelga C, Batres-Ramos S, Calés C, Lorenzo O, Perona R, Quiroga AG, Sainz B Jr, Sánchez-Pérez I. Platinum iodido drugs show potential anti-tumor activity, affecting cancer cell metabolism and inducing ROS and senescence in gastrointestinal cancer cells
Commun Biol. 2024
"These platinum(II)-iodido compounds bypass traditional DNA-targeting mechanisms to hit cancer by modulating its metabolism. Our results point to a potential therapy that combines efficacy with low systemic toxicity something rarely seen in current platinum-based treatments encouraging us to still working with these agents." Jorge Melones & Dr. Isabel Sánchez
Summary:
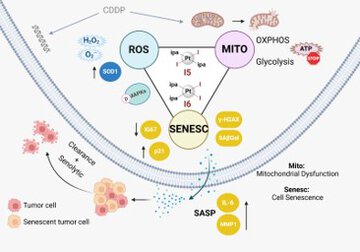
Cisplatin-based chemotherapy has associated clinical disadvantages, such as high toxicity and resistance. Thus, the development of new antitumor metallodrugs able to overcome different clinical barriers is a public healthcare priority. Here, we studied the mechanism of action of the isomers trans and cis-[PtI2(isopropylamine)2] (I5 and I6, respectively) against gastrointestinal cancer cells. We demonstrate that I5 and I6 modulate mitochondrial metabolism, decreasing OXPHOS activity and negatively affecting ATP-linked oxygen consumption rate. Consequently, I5 and I6 generated Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), provoking oxidative damage and eventually the induction of senescence. Thus, herein we propose a loop with three interconnected processes modulated by these iodido agents: (i) mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic disruptions; (ii) ROS generation and oxidative damage; and (iii) cellular senescence. Functionally, I5 reduces cancer cell clonogenicity and tumor growth in a pancreatic xenograft model without systemic toxicity, highlighting a potential anticancer complex that warrants additional pre-clinical studies.
Why do you highlight this publication?
This publication is noteworthy for advancing both conceptual and translational aspects of cancer therapy. Since the discovery of CDDP, interest in developing new platinum agents has increased, focusing on minimizing the severe side effects and the inherent resistance associated with CDDP. Among those developed, different iodido complexes have shown the capacity to overcome CDDP resistance, including our previous studies with I5 and I6. To the best of our knowledge, these are the first mechanistic studies related to the biomolecular action of platinum iodido compounds, revealing their safety in vivo and their potent anti-cancer activity in xenograft assays. In this research we demonstrated that both Pt(II) iodido complexes show antiproliferative activity through metabolic interference rather than direct DNA damage. From a preclinical development perspective, the demonstration of in vivo efficacy and the absence of systemic toxicity in a pancreatic cancer model underline I5 as a strong candidate for further therapeutic exploration.
Publication commented by:
Jorge Melones Herrero & Dr. Isabel Sánchez-Pérez
Instituto de Investigaciones Biomédicas "Sols-Morreale" IIBM-CSIC-UAM
BIOMARKERS AND PERSONALIZED APPROACH TO CANCER GROUP (BIOPAC GROUP)
IRYCIS